Twitter's search API only goes back 6-9 days. In this post I explore a way to get my full twitter history to quickly search for what I tweeted. This way I can keep using Twitter as a way to not only share but also as a reference tool for things I am learning.

There are good solutions out there to get your tweet history, see this article for example or snapbird. So there is no lack of tools, but as usual, I want to give it a try myself :)
Besides, if you want to have full control you might want to consider importing your tweets yourself. This post is a first attempt but let me say upfront that it is far from done. It is an idea to be further worked out. The nice thing is that you get a bulk of data back which is good material to ask and solve many questions your own way:
- At what time intervals do I tweet most?
- More interesting: what hashtag do I use most? With which other twitter users do I interact most?
- Simply build a search interface to search for stuff I need like a bookmarking tool (see at the end of this post).
- Etc.
All those questions you get probably answered by online apps around Twitter, but hey ... it's a learning excercise as well. An important limitation is that you can get max. 3200 tweets, for me that is ok, because I am still far below that number. It is still a lot of data though :)
A very simple Python script to start
#! /usr/bin/env python
# script to import tweet history via twitter's timeline pagination
import urllib
import simplejson
import pprint
user = "bbelderbos"
count = 100 # best result
pages = range(30)
for page in pages:
queryUrl = "https://twitter.com/statuses/user_timeline/"+user+".json?count="+str(count)+"&page="+str(page)
result = simplejson.load(urllib.urlopen(queryUrl))
#pprint.pprint(result)
for tweet in result:
print tweet['id_str']+" :: "+tweet['text'].encode("utf-8")+" :: "+tweet['created_at']
Note that user_timeline shows 200 results as max, but that doesn't mean you always get that number. I found out it is safer to just query more slices of 100!
Use: $ python import.py > all_tweets_username
Ways to enhance this script
- First off, this is one of the first scripts I wrote in Python, almost an "hello world" for me in this language. Coming weeks I am going to dive into Python and I hope to share my experience with you on this blog ...
- It is just a start to do the bulk import, an extension is needed to import new tweets via a cronjob (matching timestamp of last tweet, and append a file from that point on, etc.)
- It should except command line arguments to input the number of pages, the user, output file, etc. You see why inventing this kind of exercises for yourself, gets you up and running quickly in a new programming language ;)
- Install a database driver for python like MySQLdb and prepare DB import statements to let the script directly append the data to a DB table.
I did play around a bit more
This is one of the apps you could make with this data. I did a quick import (just text-based, so not putting it here, because the official way to go is really with "prepared statements") into mysql and I built a quick autocomplete with php, jQuery etc.:
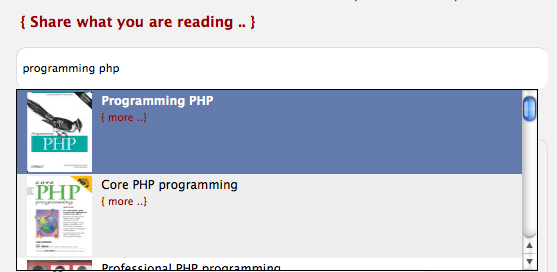
I get my tweets instantly when I start typing and when clicking on a particular tweet, it will redirect the status page with the tweet: